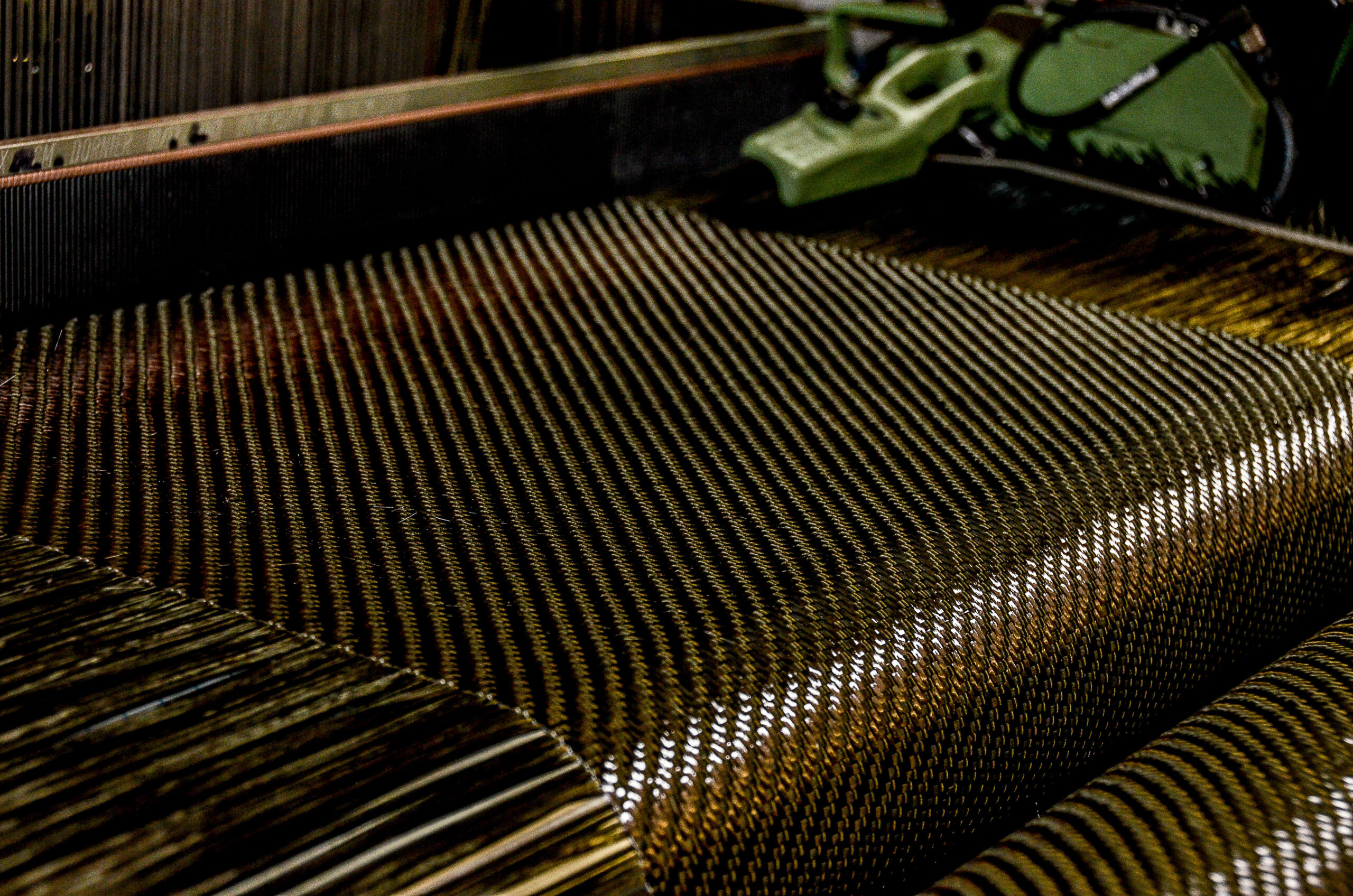
Carbon fibre has emerged as one of the most revolutionary materials in various industries, thanks to its remarkable properties and exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This article will delve into the intricacies of carbon fibre, exploring its composition, manufacturing process, applications, and environmental impact.
Understanding Carbon fibre:
Carbon fibre is a composite material known for its exceptional strength and rigidity. It is made up of thin, strong crystalline filaments of carbon, which are bonded together using a polymer matrix. This combination gives carbon fibre its unique properties, making it a desirable material in diverse sectors.
The Composition of Carbon Fibre:
Carbon Fibre Precursors:
The primary precursor used in carbon fibre production is polyacrylonitrile (PAN), although other materials like rayon and pitch can also be used. PAN-based carbon fibres are widely favored due to their high strength and excellent mechanical properties.
The Role of Polymer Matrix:
The polymer matrix in carbon fibre composites acts as a binder, holding the carbon filaments together. Epoxy is commonly used as the polymer matrix because of its superior bonding capabilities and resistance to environmental factors.
The Manufacturing Process:
Precursor Stabilization:
The manufacturing process begins with precursor stabilization. The precursor material is heated in the absence of oxygen to remove volatile components and convert it into a stable, heat-resistant form.
Carbonization:
After stabilization, the material is subjected to high temperatures in an oxygen-depleted environment. This process, known as carbonization, eliminates non-carbon elements, leaving behind a carbon-rich structure.
Post-Treatment:
The carbonized fibres undergo post-treatment, where they are processed further to enhance their mechanical properties. This step involves applying protective coatings and aligning the fibres for optimal performance.
Properties of Carbon Fibre:
High Strength and Low Weight:
One of the most significant advantages of carbon fibre is its impressive strength-to-weight ratio. It is stronger than steel while being significantly lighter, making it ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity:
Carbon fibre exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat efficiently. This property is especially advantageous in high-temperature environments.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion:
Carbon fibre has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it maintains its shape and dimensions even under extreme temperature changes.
Chemical Resistance:
Carbon fibre is highly resistant to various chemicals, making it suitable for applications in corrosive environments.
Electrical Conductivity:
Carbon fibre is electrically conductive, making it useful in applications that require electrical properties.
Applications of Carbon Fibre:
Aerospace Industry:
In the aerospace industry, carbon fibre is used to manufacture aircraft components, reducing overall weight and increasing fuel efficiency.
Automotive Industry:
Carbon fibre finds applications in the automotive sector, where it contributes to lightweight and high-performance vehicles.
Sports and Recreation:
Carbon fibre is widely used in sports equipment such as tennis rackets, bicycles, and golf clubs due to its strength and lightweight nature.
Renewable Energy:
In the renewable energy sector, carbon fibre is used to build wind turbine blades, enhancing their efficiency and durability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Carbon Fibre:
Advantages:
- Lightweight and strong
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Corrosion resistance
- Electrical conductivity
Disadvantages:
- High production costs
- Susceptible to damage from impact
- Recycling challenges
Carbon Fibre vs. Other Materials:
Carbon Fibre vs. Steel:
Carbon fibre is significantly lighter than steel while offering comparable strength, making it a preferred choice in weight-critical applications.
Carbon Fibre vs. Aluminum:
Carbon fibre exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to aluminum, making it a favored material for performance-driven applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
Carbon fibre production can have a notable environmental impact due to high energy consumption and waste generation. However, efforts are being made to improve the sustainability of the manufacturing process.
Future of Carbon Fibre:
As technology advances and production processes become more efficient, carbon fibre is expected to find even broader applications across various industries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, carbon fibre is a remarkable material with diverse applications across industries. Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, thermal conductivity, and electrical properties make it a valuable asset in aerospace, automotive, sports, and renewable energy sectors. As technology continues to evolve, the future of carbon fibre looks promising, providing innovative solutions for a wide range of challenges.
FAQs:
- Is carbon fibre stronger than steel?
- Yes, carbon fibre is stronger than steel while being significantly lighter.
- What are the primary precursors used in carbon fibre production?
- The primary precursors are polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, and pitch.
- What are the main advantages of carbon fibre?
- Carbon fibre offers high strength, low weight, excellent thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance.
- Is carbon fibre environmentally friendly?
- While carbon fibre production has some environmental impact, efforts are being made to improve its sustainability.
- Which industries use carbon fibre extensively?
- Carbon fibre is extensively used in aerospace, automotive, sports, and renewable energy industries.